R language
R is a scripting/programming language suitable for statistical computing. It offers a wide range of tools for statistical data analysis, including graphics:
It is a free software developed released under the GNU General Public License.
Download and installation
R can be extended by RStudio, an integrated development environment (IDE) which makes working in R significantly easier.
Firstly, install the core R package from the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) website:
The installation and administration guidelines are available on the R-project homepage:
https://cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/r-release/R-admin.html
After installing R, RStudio can be downloaded and installed from:
https://posit.co/download/rstudio-desktop/
We recommend installing everything with default settings.
Module 2 environment
Note: If you encounter any errors during each of installation steps you may need to temporarily disable your firewall or anti-virus software.
Module 2 contents use R version 4.3.1 "Beagle Scouts". Choose files appropriate for your operating system here https://cran.r-project.org/. For Windows version use this link to download installer: https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/base/R-4.3.1-win.exe.
If you use R on Windows some packages may need RTools software. Download and install version 4.3 of RTools from this website: https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/Rtools/rtools43/rtools.html
A recommended way to setup working environment in RStudio is to use renv (short for reproducible environment) package. Project created using these instructions will contain appropriate versions of packages used to develop and run scripts in Module 2.
Instructions
Step 1. Before creating R environment make sure you have downloaded Module 2 data packages from Zenodo.
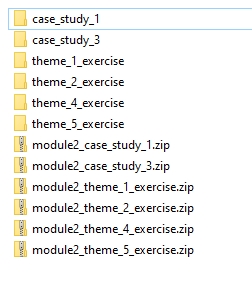
Step 2. Create a new catalogue and name it module2. Move the downloaded data packages to this folder. Unzip the data inside this catalogue and remove module2_ from the folder names. This is what your module2 catalogue should look like after completing Step 2.
Step 3. Launch RStudio
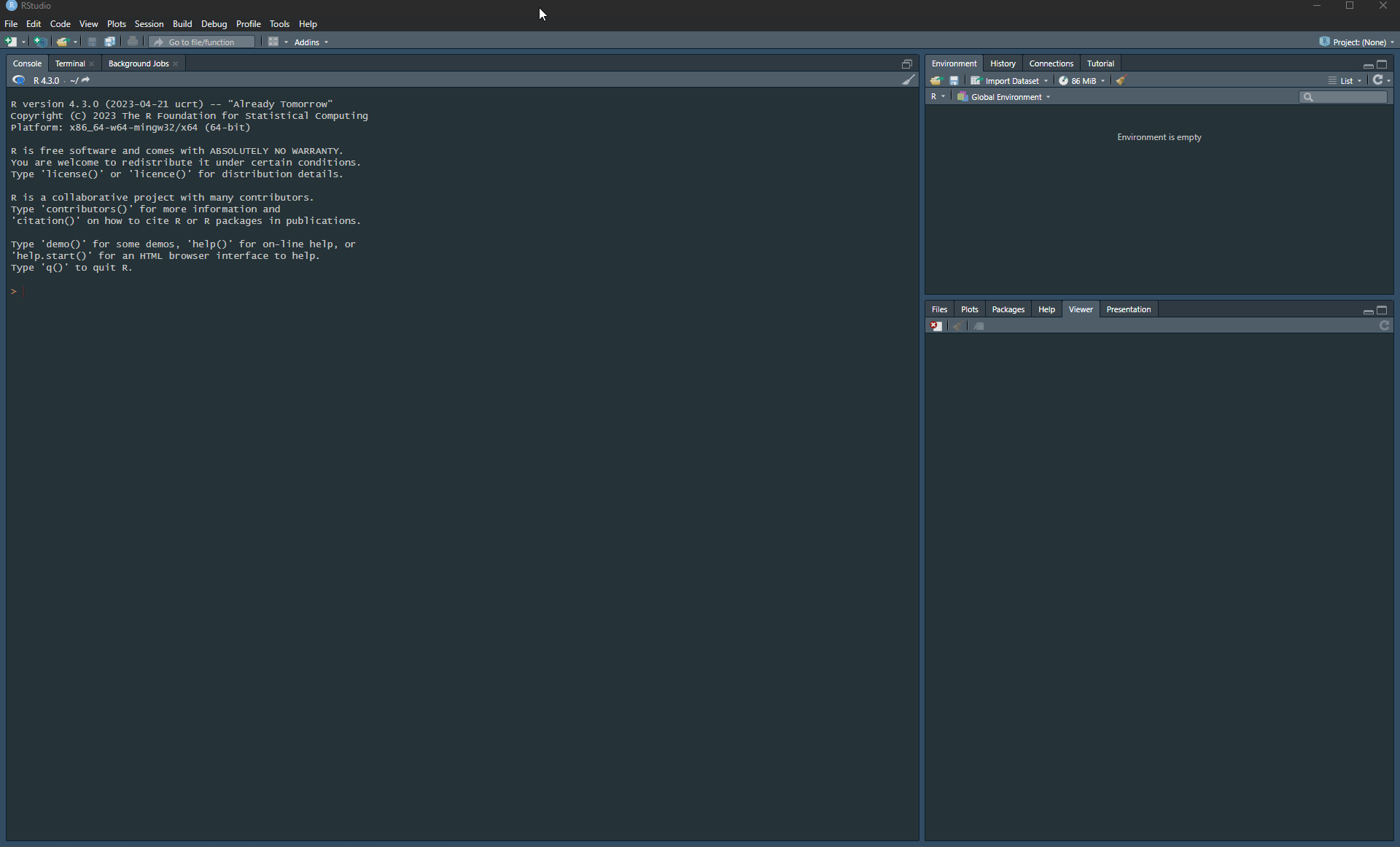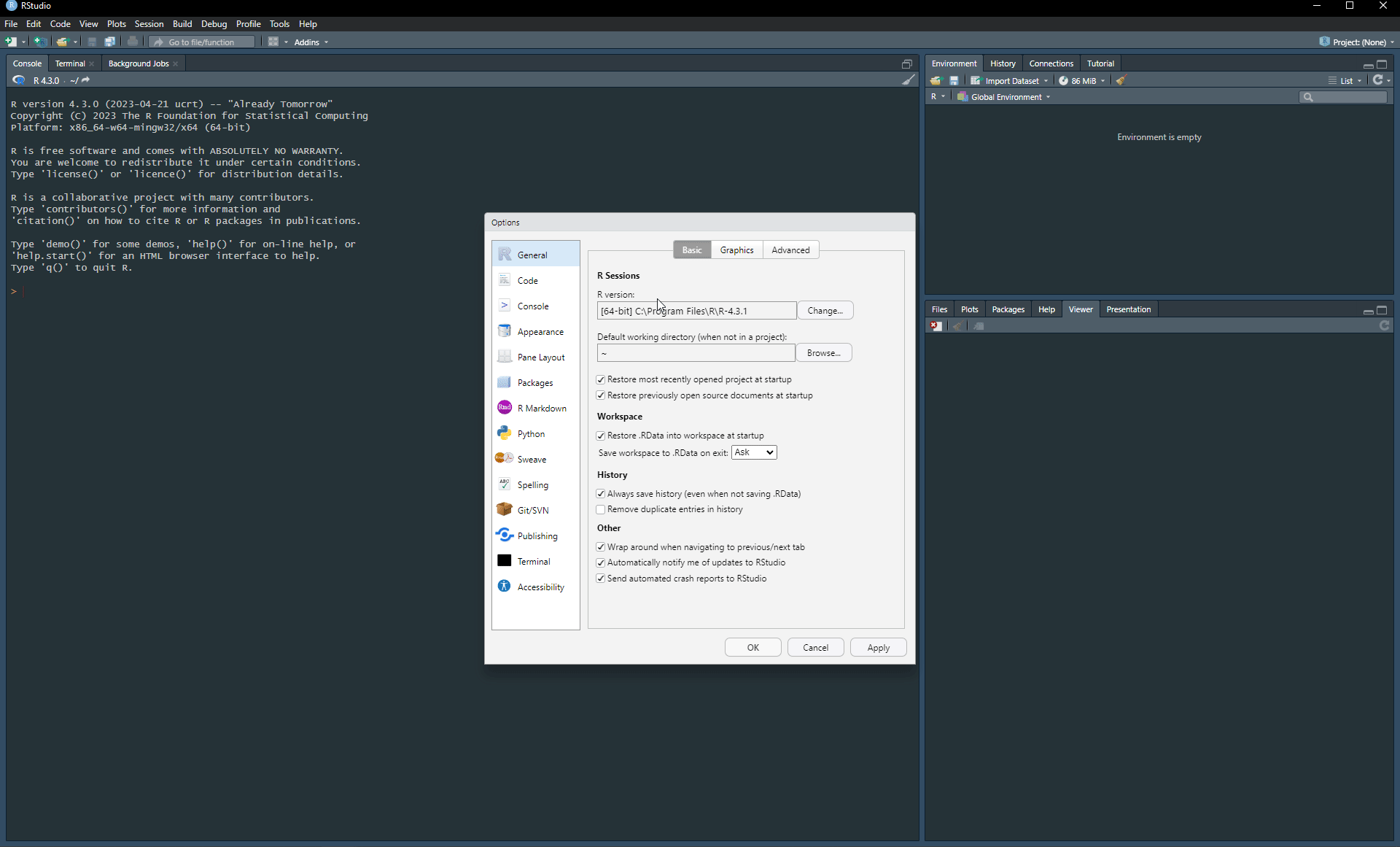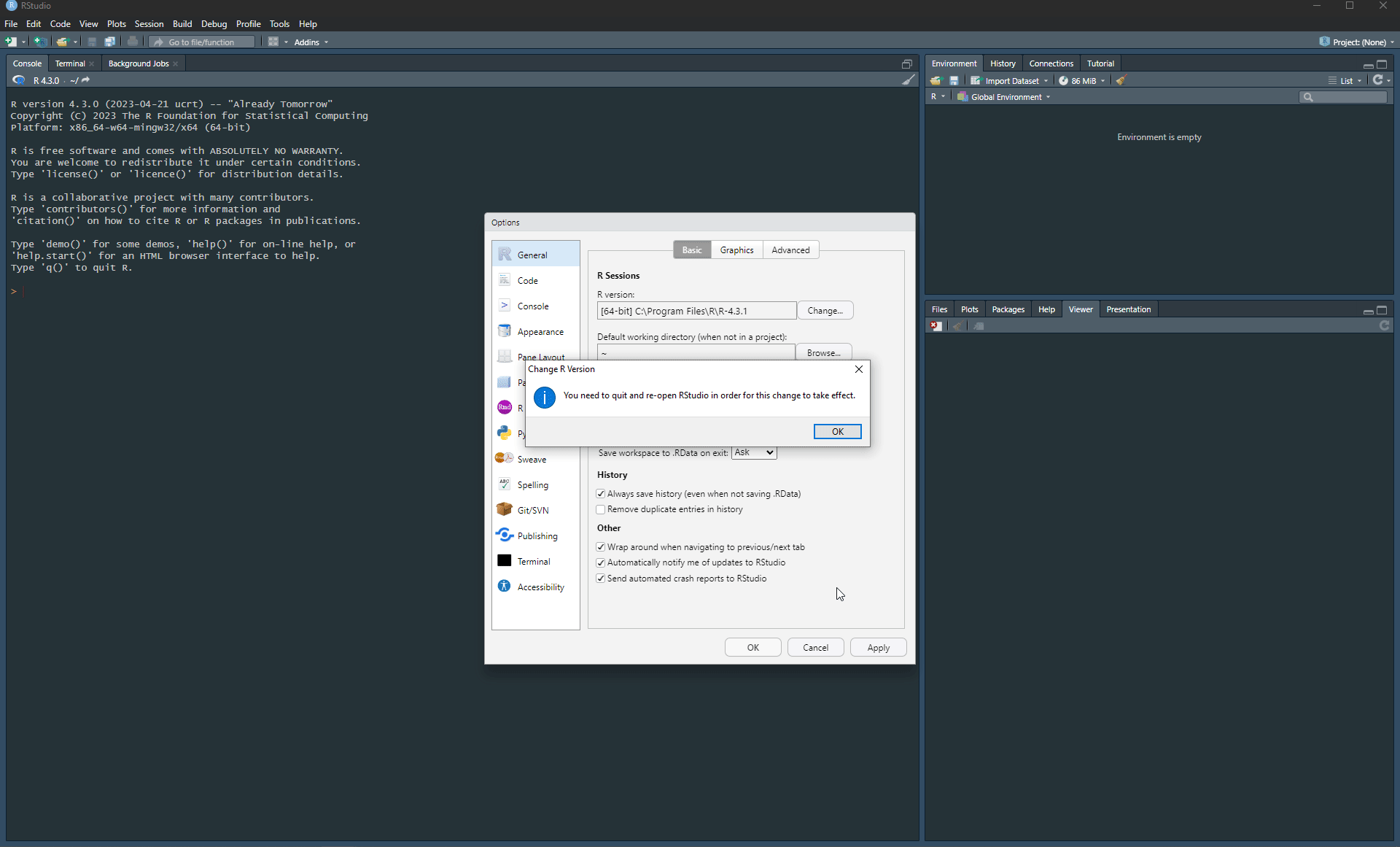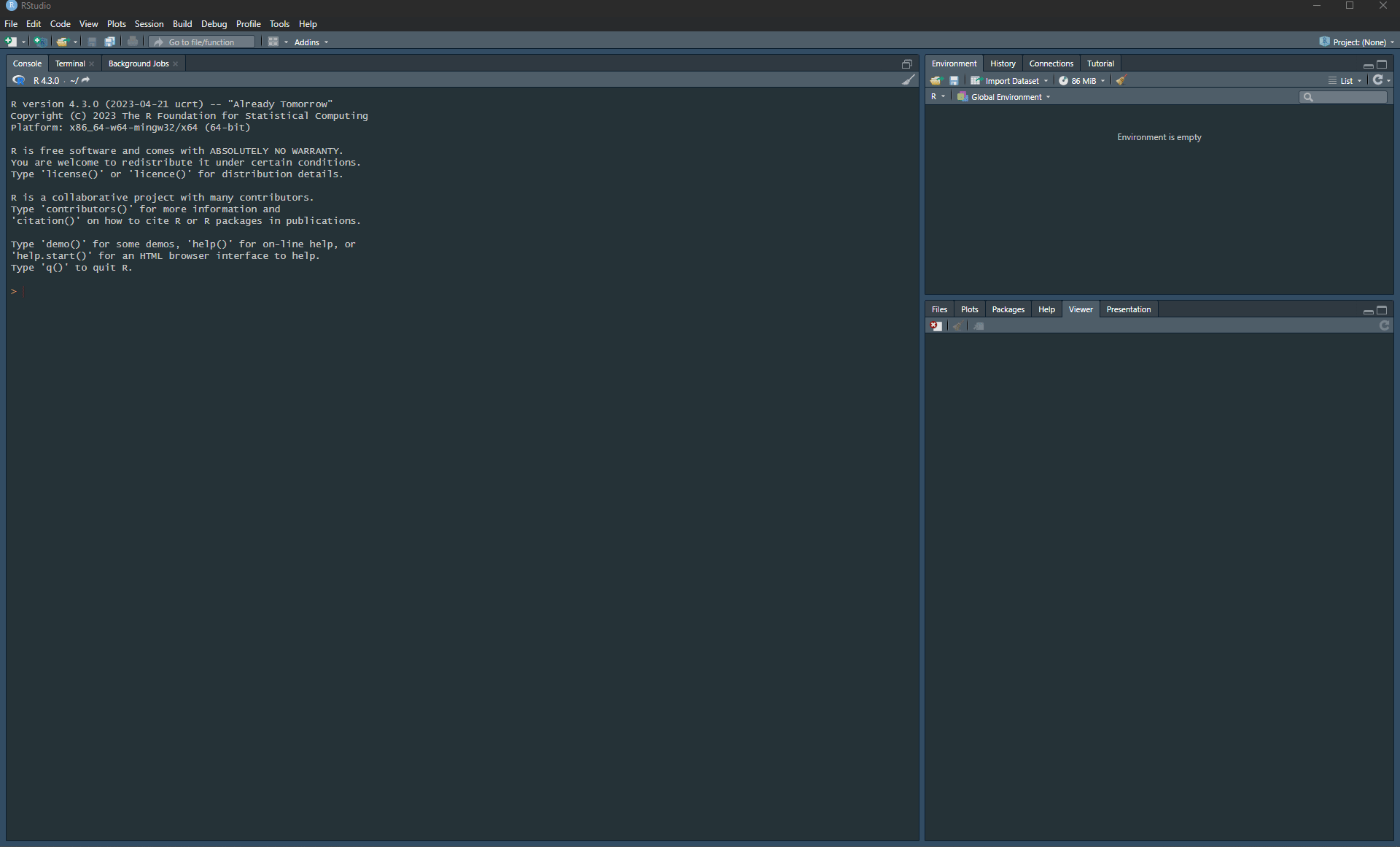
Step 4. Check out you R version. After you launch RStudio the first line in the console should read
R version 4.3.1 (2023-06-16 ucrt) -- "Beagle Scouts"
If you have different R versions installed make sure to change version to R 4.3.1 as shown below
Click on the GIF to open full size version in a new tab
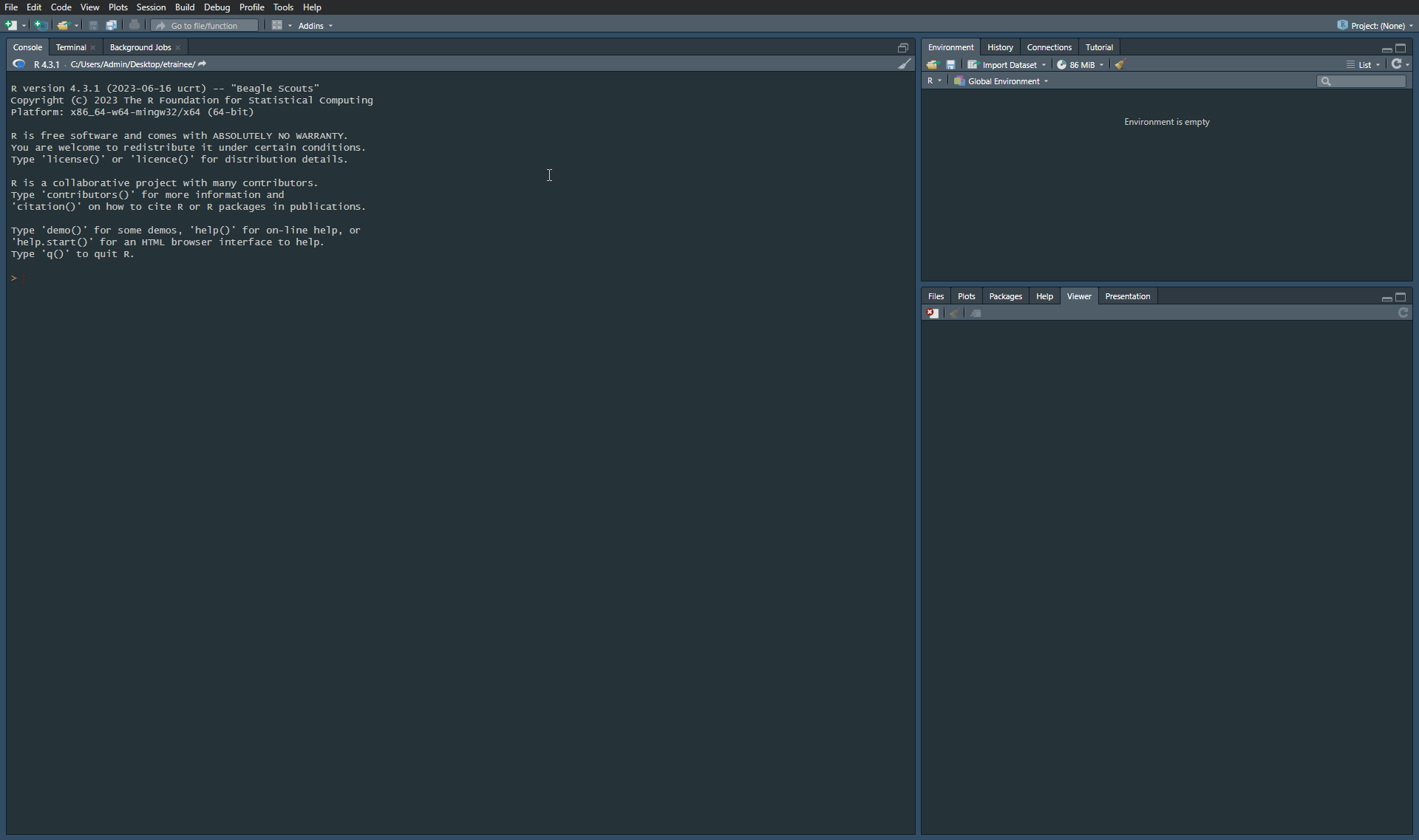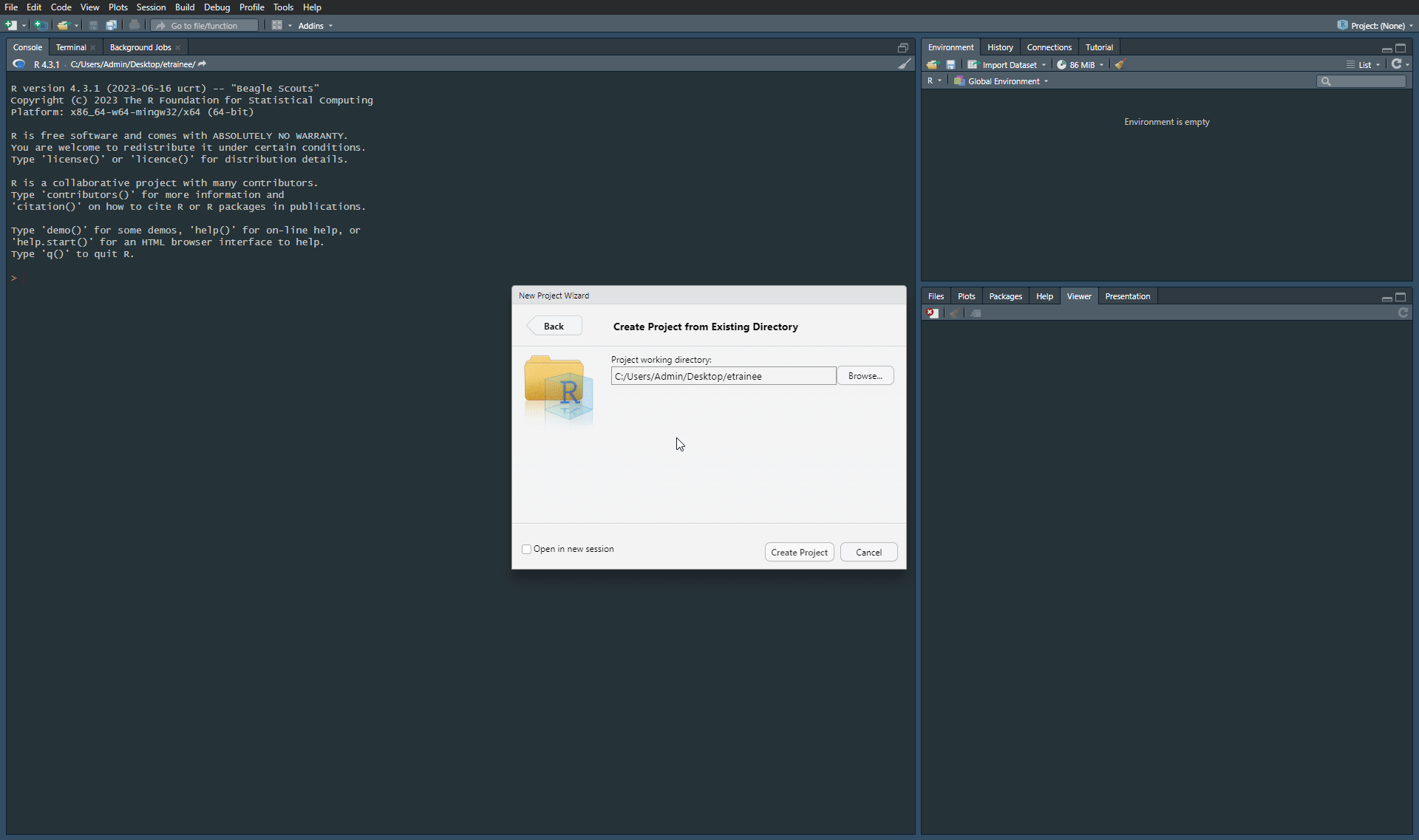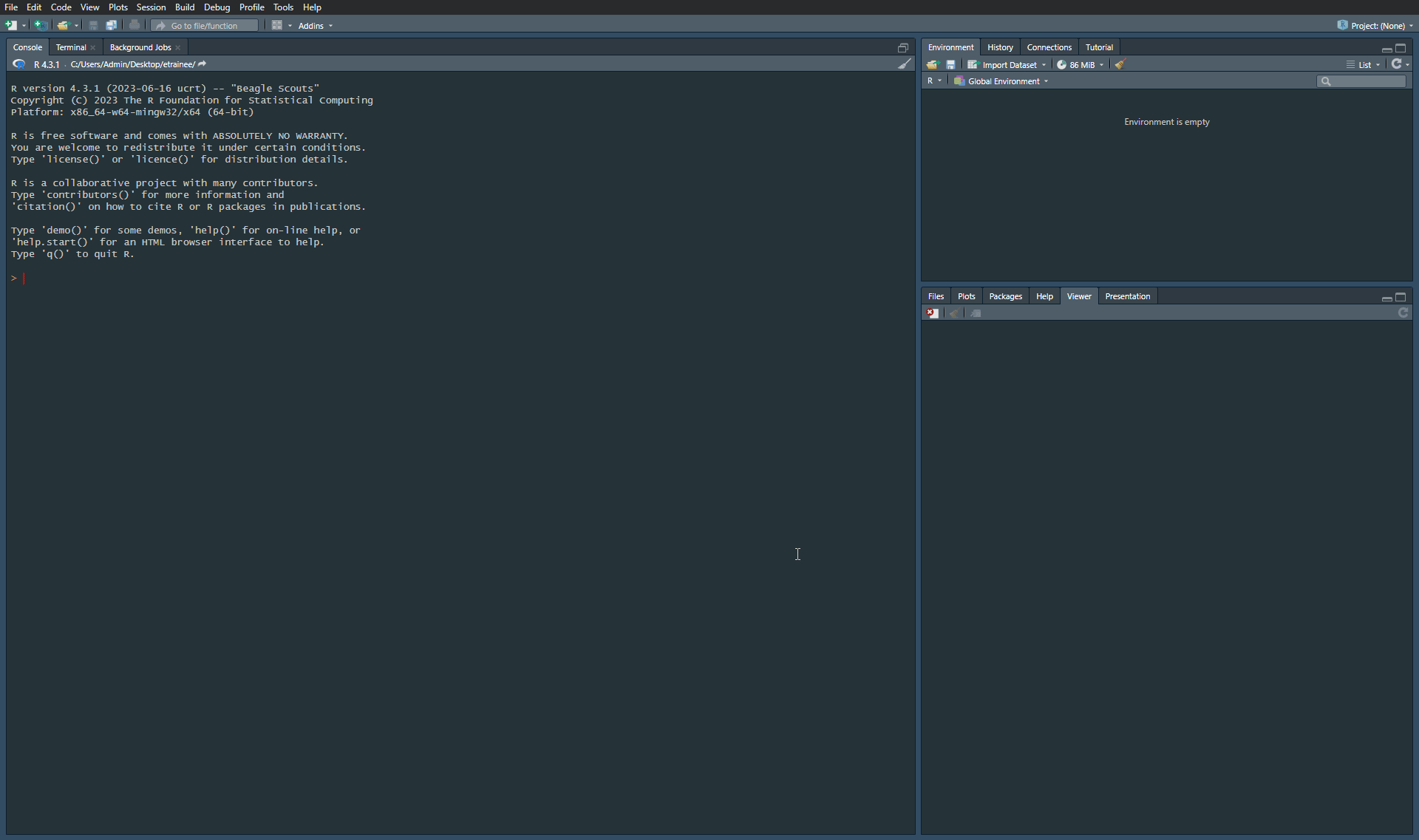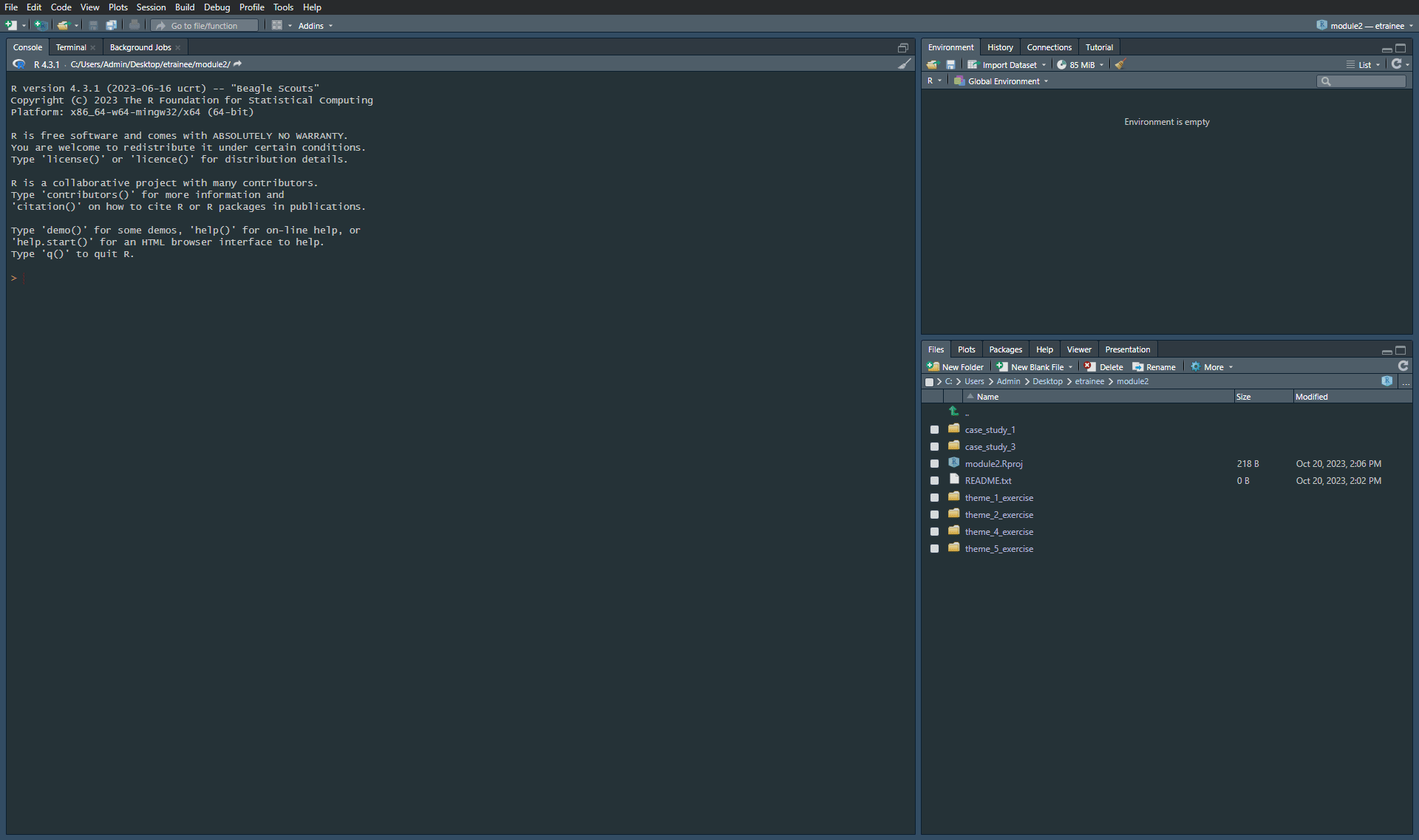
Step 5. Create a New Project. Connect it with existing directory. Change the path to module2 data catalog, in which you unzipped packages with data.
Click on the GIF to open full size version in a new tab
Step 6. Install renv using install.packages("renv") command in the console
Step 7. Load renv package executing library(renv) in the console
Step 8. Use renv::init() to initialize renv within a project created in Step 5.
Step 9. Replace the default renv.lock file inside the project folder with the downloaded one: download renv.lock
Step 10. Use renv::restore() to install specific package versions recorded in the lockfile. When prompted type y in the console to install packages recorded in renv.lock file
By following these steps you ensure that you will work on the most up-to-date environment that the contents of Module 2 use. To work in a project just open .Rproj file. This action will open RStudio with you environment setup.
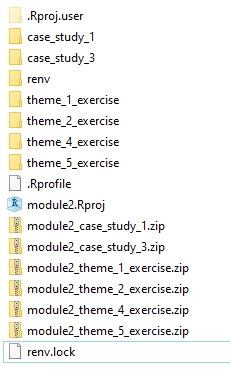
If you followed the recommended steps this is the content of module2 folder you should be seeing. Note that after unzipping you can safely remove .zip packages from this folder.
Note: To ensure compatibility and consistent results across exercises, please adhere to the following specified versions of R and packages. Running exercises on different versions may lead to unexpected results and potential inconsistencies and errors.
Getting started / external material
If you are new to R / programming, consider going through one or more of these tutorials first:
Introduction to the R language and statistical analysis:
https://cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/r-release/R-intro.html
Instructions on how to import and export data using R and respective packages:
https://cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/r-release/R-data.html
Friendly introduction to R programming and using R for data analysis can be found in these books:
'Hands-On Programming with R' by Garrett Grolemund
'R for Data Science (2e)' by Hadley Wickham, Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel, and Garrett Grolemund
'Geocomputation with R' by Robin Lovelace, Jakub Nowosad and Jannes Muenchow